IoT Networking Coursera Quiz Answers
Hello Friends in this article i am gone to share Coursera Course: IoT Networking by University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign | IoT Networking Coursera Quiz Answers with you..
Enroll Link: IoT Networking
IoT Networking Coursera Quiz Answers
Also visit: IoT Communications Coursera Quiz Answers
Week 1 and 2 Quiz Answers
Question 1)
According to a recent study, roughly what percentage of “smart” devices are vulnerable?
- 87%
- 5%
- 40%
- 25%
Question 2)
What is the maximum amount of failures that a ring topology with n nodes tolerate before it is possible for the network to have 2 connected components?
- 2
- 1
- 0
- n
Question 3)
All interfaces of one device use the same MAC address.
- True
- False
Question 4)
What is the order you encapsulate data in OSI?
Note: L’s are layers – so L3 means layer 3
- L2(L3(L4(x)))
- L4(L3(L2(x)))
Question 5)
What’s the main purpose of a TTL field in an IPv4 header?
- To mitigate routing loops.
- To mark packets with priorities.
- To encode options such as fragmentation.
- To encode ASCII text as data that can be transmitted over a network.
Question 6)
Devices on different IP subnets are commonly configured on the same VLAN.
- True
- False
Question 7)
Which layer encodes the VLAN tag?
- HTTP
- Ethernet
- Physical layer
- TCP
- IP
Question 8)
Why does Ethernet benefit from a spanning tree protocol?
- It proactively disseminates routes to destinations in the network.
- It removes loops that could occur when each node broadcasts a data packet.
- The spanning tree could provide a faster route than the physical connections would allow.
- It enables configuration of VLANs, which allow a single physical network to be divided up into multiple virtual networks.
Question 9)
What is the purpose of DHCP?
- To look up the MAC address associated with an IP address.
- To look up the IP address associated with a MAC address.
- To transport data packets at one of the layers of the OSI model.
- To assign configuration information to end hosts, including IP addresses.
Question 10)
What is the purpose of ARP?
- To look up the IP address associated with a MAC address.
- To look up the MAC address associated with an IP address.
- To assign configuration information to end hosts, including IP addresses.
- To transport data packets at one of the layers of the OSI model.
Question 11)
What is a response code for in HTTP?
- To encode the content of a response.
- To indicate the version of HTTP being used.
- To indicate the status of a server or type of request.
- To indicate the resource being referred to by the request.
Question 12)
What are “sockets” in the context of network programming?
- To indicate the status of the server the application is communicating with.
- An API used to allow the application to communicate via the network.
- Ports on a router that are used to plug in cables.
- Numbers in the TCP/UDP header which define which application running at the remote host the packet is destined to.
Question 13)
What sockets function call is used to perform a DNS lookup?
- connect(sockfd, &their_addr)
- getdnslookup()
- socket()
- struct hostent;
- gethostbyname()
Question 14)
When a host sends a TCP data packet to a host outside the local subnet (multiple IP-level hops away), which of the following pieces of information does it need to put in the packet?
- The TCP port of the application running at the final destination.
- The IP address of the final destination.
- The IP address of the default gateway.
- The TCP port of the application running at the default gateway.
- The MAC address of the default gateway.
- The MAC address of the final destination.
Question 15)
When constructing a typical moderate-to-large-scale network deployment, such as in a smart building or smart city, what technologies would be deployed where?
- Ethernet core, IP access, Zigbee/Wifi to devices.
- IP core, Ethernet access, Zigbee/Wifi to devices.
- Wifi core, IP access, Ethernet to devices.
- Zigbee core, IP access, Ethernet to devices.
- Zigbee core, Ethernet access, IP to devices.
- Ethernet core, Zigbee access, IP to devices.
Question 16)
Where are sockets implemented?
- Within the NIC’s firmware.
- Within the IP layer in the kernel.
- Within the network device driver.
- Within a library and set of system calls.
- Within the Ethernet layer in the kernel.
- Within the TCP/UDP (transport) layer in the kernel.
Week 3 and 4 Quiz Answers
Question 1)
Consider the following figure:
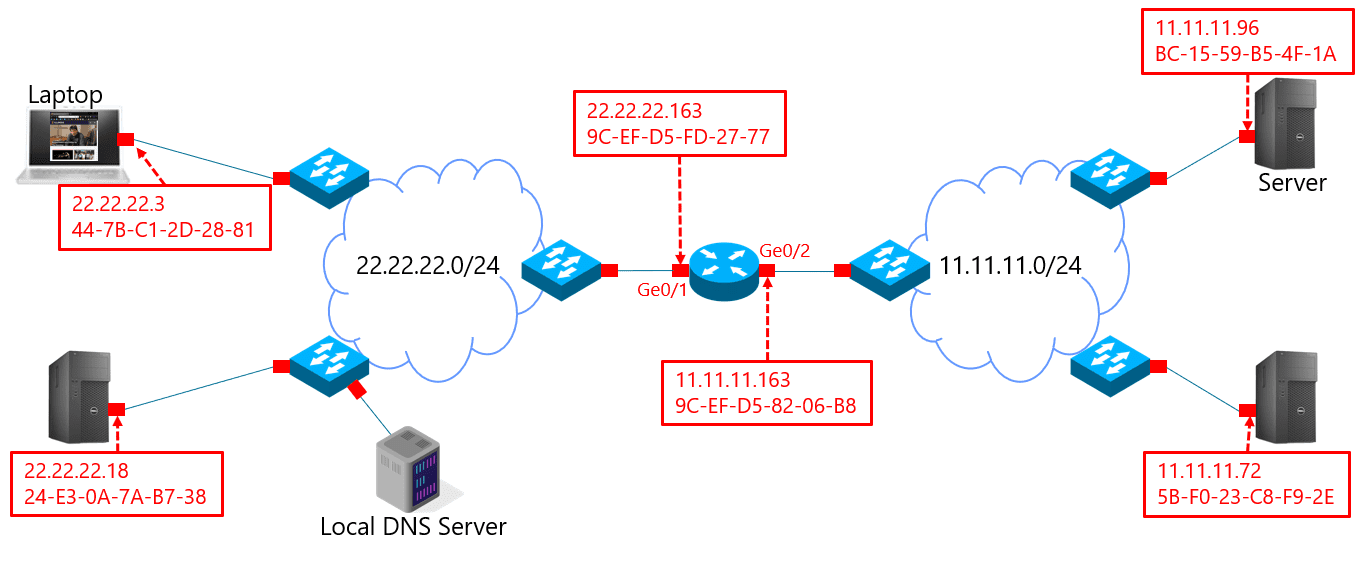
Suppose the server in the lower left sends a data packet to the server in the lower right. Write out the packet headers at each hop.
How many times does the MAC address change (ie., how many MAC addresses appear in the packet’s header over time)?
- Zero.
- Three.
- One.
- Two.
- Four or more.
Question 2)
Consider the following figure:
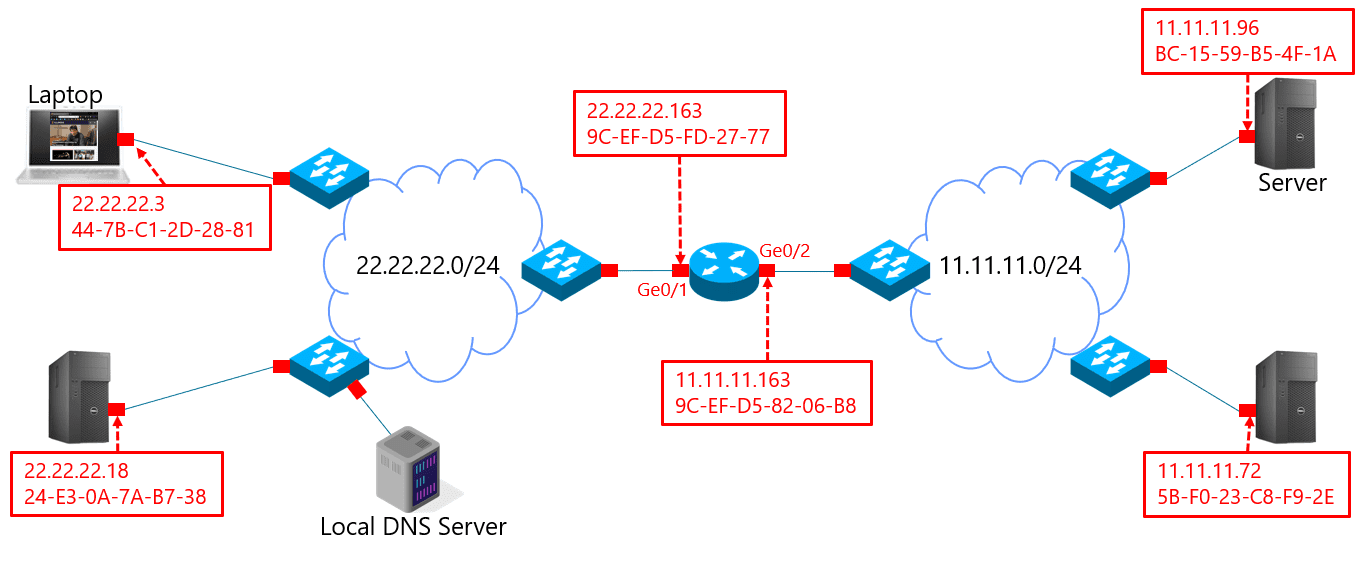
Suppose the server in the lower left sends a data packet to the server in the lower right. Write out the packet headers at each hop.
Assume all ARP caches are empty. How many ARP lookups are performed?
- Two.
- One.
- Zero.
- Three
- Four or more.
Question 3)
Why are network cores Layer 3 instead of Layer 2?
- Improved scaling
- To enable VLANs to span the core
- To enable firewalling on both layer 2 and layer 3
- To enable IP packets to be sent across the network core
- Network cores are not layer 3, as they allow layer 4 packets to be transferred across them
Question 4)
Why are ring topologies often used in wide-area campus networks?
- Performance
- To enable any source to route to any destination
- The optical signal traverses continuously around the loop; packets are “affixed” to the signal as it propagates around, then removed when they reach the egress router closest to the destination
- To enable misrouted packets to traverse back to the source
- Resilience
Question 5)
Which layer uses broadcast to discover paths to destinations?
- Layer 5
- Layer 6
- Layer 3
- Layer 4
- Layer 7
- Layer 1
- Layer 2
Question 6)
Which of the following is a proper way to implement segmentation in a computer network?
- Firewall rules
- VLANs
- VRFs
- All of the options are correct
Question 7)
What happens if two hosts share the same IP address, but not the same MAC address on a LAN?
- They would both respond to ARP request messages
- It is impossible for two hosts to share the same MAC address, are they are allocated via a mechanism that prevents overlaps
- They would both pass a message sent to their shared MAC address up to layer 3 kernel code in their respective operating systems
- A gratuitous ARP would be performed, and upon detecting an address collision, the host would select a new MAC address
Question 8)
You’re running out of network segments. You’re using very old Ethernet switches. If you have the budget, you should replace your LAN switches with ones that support:
- IEEE 802.1ad (QinQ)
- IEEE 802.11
- IEEE 802.11n
- IEEE 802.1q
Question 9)
Which of the following can be learned via DHCP?
- Mapping between destination’s MAC and IP address
- DNS server IP address
- MAC address
- URL
- Autonomous System number
Question 10)
Is encapsulation performed in the application (user space) or within the operating system’s kernel?
- Kernal Space
- Both options are correct
- Neither option is correct
- User space
Week 1 Honors Checklist Quiz Answers
Question 1)
Check what applies to you (pick all that apply).
- I have finished the lab assignment for week 1 honors section.
- I have posted the discussion forum entry for week 1 honors section and responded to at least two entries of my peers.
- I certify that I have completed these tasks to my own and best efforts, and that I am able to explain what I did.
Question 2)
If you did the lab, you should know the answer to this question. In this step of the lab, we are using firewalls. What security strategy is mentioned that can be implemented by using firewalls?
- Fixed-Width Denominator
- Multiple End-Points
- Perimeter
- UDP Method
Week 2 Honors Checklist Quiz Answers
Question 1)
Check what applies to you (pick all that apply).
- I have finished the lab assignment for week 2 honors section.
- I have posted the discussion forum entry for week 2 honors section and responded to at least two entries of my peers.
- I certify that I have completed these tasks to my own and best efforts, and that I am able to explain what I did.
Question 2)
If you did the lab, you should know the answer to this question. In this step of the lab, we use Wireshark. What is used to run Wireshark directly on the Raspberry Pi?
- Bluetooth
- WiFi
- HDMI
- USB
Week 3 Honors Checklist Quiz Answers
Question 1)
Check what applies to you (pick all that apply).
- I have finished the lab assignment for week 3 honors section.
- I have posted the discussion forum entry for week 3 honors section and responded to at least two entries of my peers.
- I certify that I have completed these tasks to my own and best efforts, and that I am able to explain what I did.
Question 2)
If you did the lab, you should know the answer to this question. In this step of the lab, what command is used to get information on versions of wifi network protocols supported by your wireless network interface, as well as signal strength?
- iwconfig
- ifconfig
- ipconfig
- traceroute
Week 4 Honors Checklist Quiz Answers
Question 1)
Check what applies to you (pick all that apply).
- I have finished all lab assignments of this course.
- I have posted the discussion forum entry for week 4 honors section and responded to at least two entries of my peers.
- I certify that I have completed these tasks to my own and best efforts, and that I am able to explain what I did.
Question 2)
If you did the lab, you should know the answer to this question. In this step of the lab, what is listed as one of the important parts of the lab?
- Asymmetric Encryption
- IpSec Encapsulation
- Packet Inspection
- Virtual Private Networks
