Wired Connections
Hello Friends in this article you will learn about Wired Connections.
Also visit: Networks Types and Topologies
After reading this article, you will be able to:
- Identify wired connection types.
- Understand which wired connection types are older and which are newer.
- List the pros and cons of wired connection types.
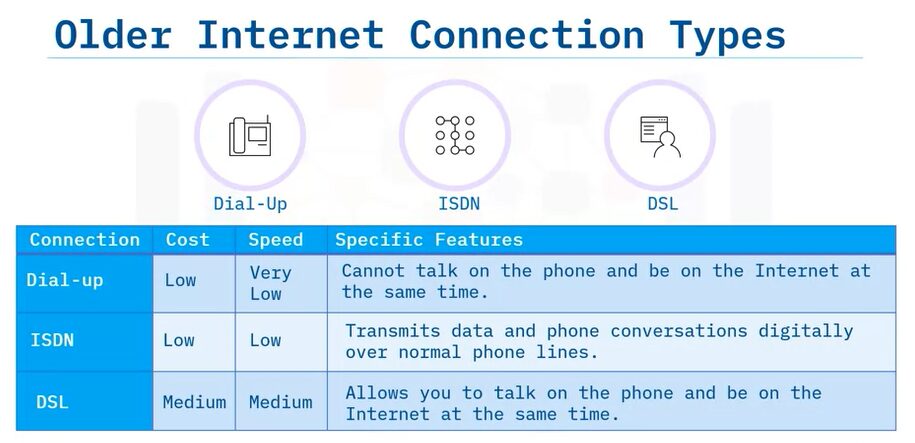
Older internet connection types
Older internet connection types that use phone lines are:
- Dial-up: Cannot use the phone and Internet at the same time.
- ISDN or integrated services digital network: Transmits data and phone conversations digitally.
- DSL or digital subscriber line: Faster than dial-up, can use the phone and Internet at the same time.
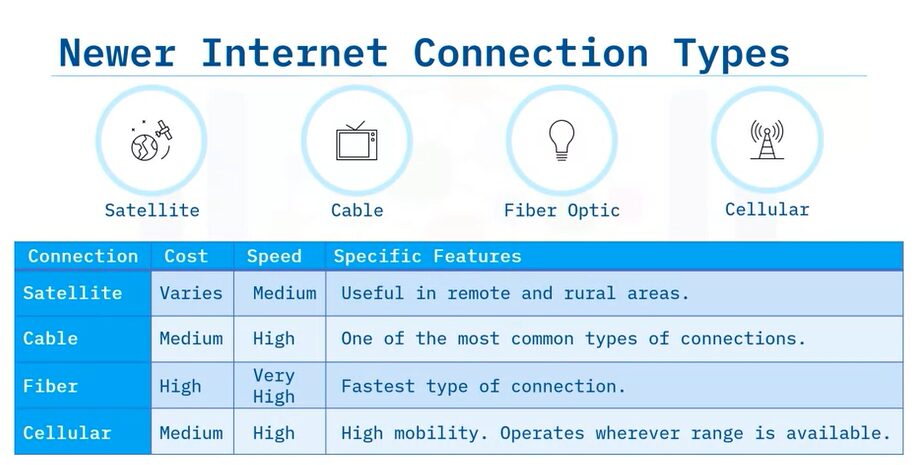
Newer internet connection types
Newer internet connection types are:
- Satellite: relies on communication satellites. Popular in remote and rural areas.
- Cable: uses the same coaxial cables as cable television. One of the most common connection types.
- Fiber Optic: relies on fiber-optic cables to transfer data with light waves instead of electricity. The fastest connection type. Cellular: uses the same channels as cellular phones. Allows connection almost anywhere.
Wired networking
Wired networking refers to the use of wire connections that allow users to communicate over a network. Most computer networks still depend on cables or wires to connect devices and transfer data. Dialup: Requires a modem and phone line to access the internet. Popular in the past but has steadily been replaced by broadband internet services.
| Pros | Cons |
| Available to everyone with a phone line | Very slow. |
| computer, and modem | Unsuitable for gaming or downloading media. |
| Can serve rural or remote areas | Cannot use the phone at the same time. |
| Low cost. | |
| Easy setup. |
DSL or digital subscriber line: Connects to the internet using a modem and two copper wires within phone lines to receive and transmit data. Slower than cable and fiber.
- Pros: Faster than dial-up. Inexpensive. Dedicated connection. Provides Wi-Fi. Transmits data using existing phone lines.
- Cons: Slow and weak over long distances. Speed rarely exceeds 100 Mbps. Not always available.
| Pros | Cons |
| Faster than dial-up. | Slow and weak over long distances. |
| Inexpensive. | Speed rarely exceeds 100 Mbps. |
| Dedicated connection. | Not always available. |
| Provides Wi-Fi. | |
| Transmits data using existing phone lines. |
Cable: Delivers Internet via copper coaxial television cable. It is the best option for fast and reliable Internet (if you don’t have access to fiber optic).
| Pros | Cons |
| Uses existing TV infrastructure to reduce cost. | Bandwidth sharing (neighbors). |
| High speeds rival pure fiber in ideal implementations. | Slow during peak times. |
| Higher bandwidth than DSL in most cases. | Upload speeds much slower than download. |
| Speeds not substantially affected by distance from ISP office. | Susceptible to electromagnetic interference. |
| Lower latency than DSL in most cases. |
Fiber Optic cables: Transmit data by sending pulses of light across strands of glass (up to 200 Gbps). Fast, reliable, and consistent. This connection rarely lags, which makes it perfect for HD streaming or online gaming.
| Pros | Cons |
| Efficient. Reliable connection. | Expensive. |
| Great for long distances. | Not available everywhere. |
| Fast speeds (up to 200 Gbps). | |
| Best for streaming and hosting. |
Summary
In this article, you learned that: Older Internet connection types, like Dial-Up, ISDN, and DSL, are low-cost and offer low to medium speed. Newer Internet connection types, like Satellite, Cable, Fiber Optic, and Cellular, are higher in cost, but offer useful features such as higher speed and mobility. And wired connections like cable and fiber optic have gotten faster and stronger, but older technology like dial-up and DSL still works when you need it.

