What is a SOHO network
Welcome to “Configuring a Wired SOHO Network.” After reading this article, you will be able to understand What is a SOHO network and:
Also visit: Cables and its types
- Describe the features of a SOHO network.
- List the requirements for setting up a SOHO network.
- Explain how to configure, test and troubleshoot a SOHO network.
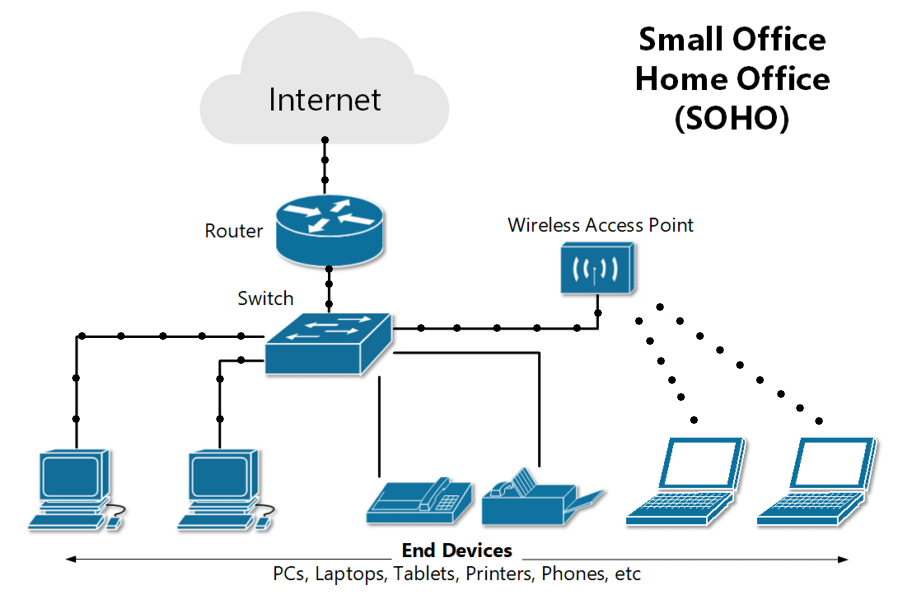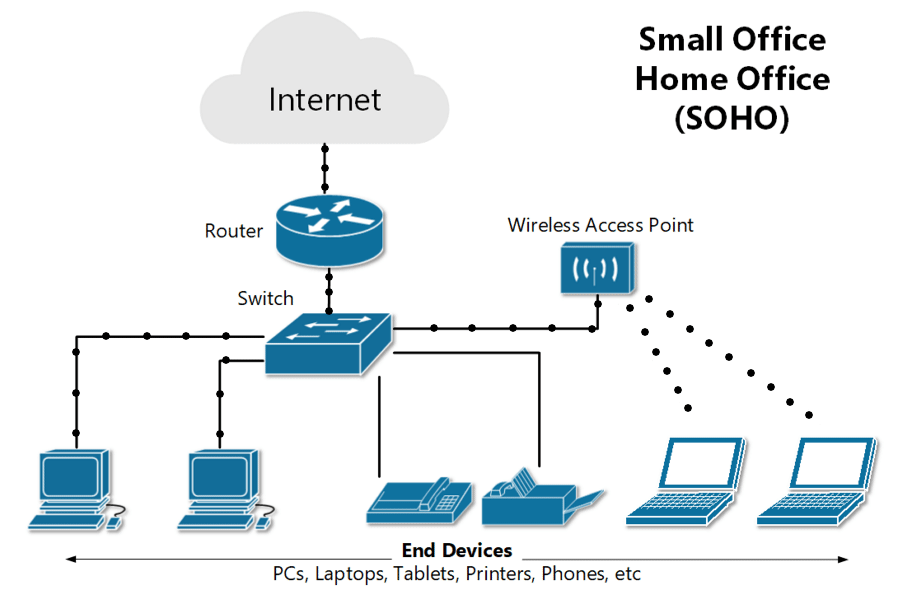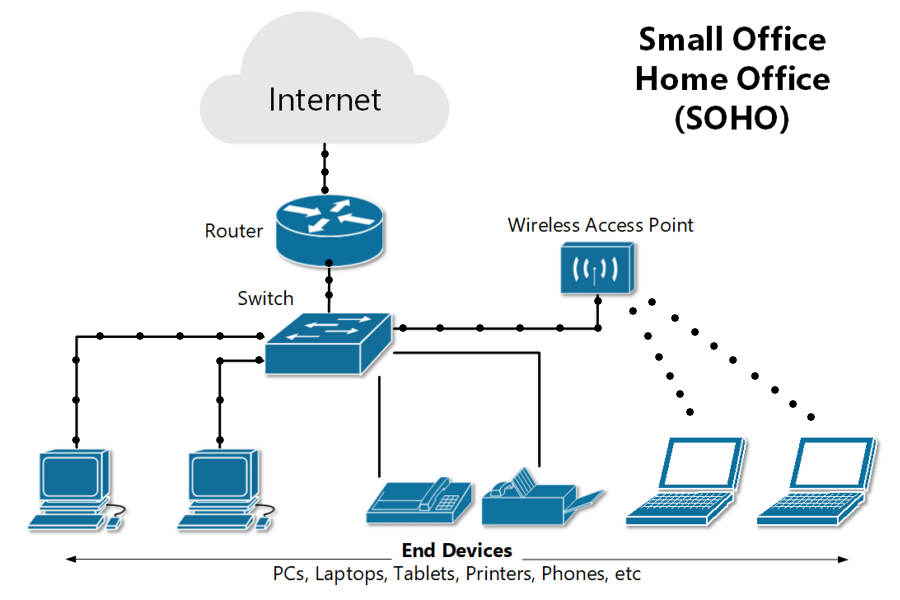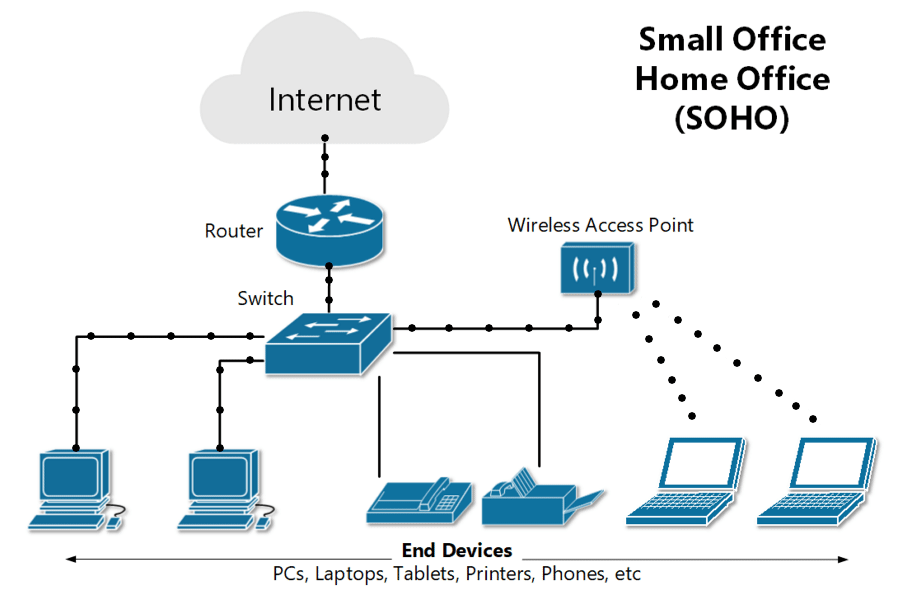
What is a SOHO network ?
A small office/home office, or SOHO, network is a local area network, or LAN, with less than 10 computers that serves a small physical space with a small number of employees or home users. It can be a wired Ethernet LAN or a LAN made of both wired and wireless devices.
A typical wired SOHO network includes a router with a software-based firewall, a switch with 4 to 8 Ethernet LAN ports, a printer, and several desktops or laptops. SOHO networks often use email, website, and cloud subscription services since maintenance and reliability are included. Internet is provided via cable, DSL, or ISDN. Basic equipment maintenance is easy since there are only a handful of devices and cables to consider.
Setting up
When setting up a SOHO network, knowing the compatibility requirements is very important. The hardware, software, adapter cards, and cables all need to be compatible for the network to function properly. Before setting up any SOHO network, review and confirm everything in your plan to ensure a successful installation.
- SOHO networks need a switch to act as the hub of the network. If Internet is desired, a router can be added or used instead.
- SOHO routers often have other integrated features, like a cable or DSL modem, switch ports, and a built-in firewall.
- A modem provides an Internet connection. Ethernet Cables provide a wired connection. Category 5, 5E, and 6 cables are the current standard.
- A router automatically assigns IP addresses to each device on the network, which is necessary if you intend to share your Internet connection with all the connected devices. And a SOHO network switch typically allows 4 to 8 connected devices to talk to each other but does not assign IP addresses or provide Internet.
- Switches are best used to expand the number of LAN ports available on the network, since the number of ports on a router can be limited.
Set up the hardware in a SOHO network
Set up the hardware in a SOHO network using the following steps:
- Plug the switch or router into a power source.
- Connect the switch to the router (if necessary). If you’re using a switch and a router, plug one end of an Ethernet cable into any LAN port on the router and the other into any LAN port on the switch. This will expand the network to the rest of the LAN ports on the switch.
- Connect your modem to your router (if necessary).
- If you’re sharing an Internet connection from a modem, connect the modem to the WAN/INTERNET port on the router. This is usually a different color than the other ports.
- Connect your computers to open LAN ports.
- Use Ethernet cables to connect each computer to any open LAN port on your router or switch. Keep devices close to the router or switch since Ethernet doesn’t transfer data reliably over long distances (100 meters maximum).
Configure router settings
The next steps are to configure router settings:
Log in to router settings: Enter “ipconfig” into a command prompt window to find your router’s public IP address. It will be listed next to “default gateway.”
Enter it into a browser and log in Update user name and password: All routers have default administrator user names and passwords. Anyone with access can change the admin password or other settings and even lock you out. To improve security, always change the default user name and password.
Update firmware: Updating router firmware solves operational problems and enhances security. Check the manufacturer website for available firmware updates Download and install if your firmware is not up to date As you configure, remember that the model number, revision number, and login defaults are printed on the router or its manual, and that the local or private IP address of any router is usually set to 192.168.1.1.
The security of a wired SOHO network primarily depends on a firewall since all data packets in a wired network travel through secure Ethernet cables. Most broadband routers have a built-in firewall and additional software firewalls can be installed on individual machines. Servers and hardware have built-in Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and Network Address Translation actions. DHCP servers use IP addresses to provide network hosts while NAT maps a public IPv4 address to private IP addresses. SOHO network administrators don’t have to configure firewall or server settings unless more than a basic setup is required.
User account setup is included in most operating systems. Apple or Linux setup steps will vary. In Windows, open the Control Panel and select User Accounts. Configure your account and settings. Add or configure other users by selecting Manage another account. If you wish to add and configure local users and groups, search and select Computer Management, then select “Local Users and Groups.” In Windows 10 or higher, Device Manager allows you to add devices to a network, set default printers, and more. If the network firewall uses MAC filtering, be sure to modify the whitelist for each authorized client.
Network performance depends on Internet strength, cable specification, installation quality, connected devices, and network and software settings. Test and troubleshoot to ensure proper network performance. To troubleshoot performance: run security tools, check for updates, restart devices, run diagnostics, reboot the router or modem, and check equipment for damage.
Summary
In this article, you learned that: Wired SOHO networks have a router, switch, printer, and connected devices. Compatibility requirements are very important. Physical setup includes connecting the router to the modem, and a device to the router. Ipconfig shows your router’s public IP address. Router settings are configured from a browser. And groups and users are configured through the Control Panel and Computer Management Tools.

