Project Management Foundations, Initiation, and Planning Quiz Answers
In this article, I will be sharing the complete set of 100% correct quiz answers for the Coursera course Project Management Foundations, Initiation, and Planning, offered by SkillUp EdTech. This course is designed to provide valuable insights into the core principles of project management, and these answers will serve as a helpful resource for those seeking to enhance their understanding and successfully complete the quizzes.
Course link: Project Management Foundations, Initiation, and Planning
Module 2 Graded Quiz: Traditional Project Management Quiz Answers
Question 1)
The team is classifying various project management models as either adaptive or predictive. Which of the following models would most closely meet the definition of adaptive?
- Critical chain
- Kanban
- Waterfall
- Critical path
Explanation: Kanban is an adaptive project management model that focuses on flexibility, continuous delivery, and efficiency, making it well-suited to changing requirements.
Question 2)
Ralph Stacey developed a method to objectively determine the type of lifecycle to apply to a project. Which of the following two answers are parameters Stacey recommends in making this decision?
- Technical degree of uncertainty
- Personnel capacity
- Risk exposure
- Requirements uncertainty
Explanation: Stacey’s model evaluates technical and requirements uncertainty to determine whether to use a predictive or adaptive lifecycle.
Question 3)
A project sponsor wants to establish an agile methodology to manage certain projects. Which of the following two key roles are essential to the success of this initiative?
- Product owner
- Scrum master
- Project manager
- Program manager
Explanation: Agile methodologies like Scrum emphasize roles such as the product owner, who prioritizes the backlog, and the scrum master, who facilitates the agile process.
Question 4)
A customer requests frequent deliveries during an inventory management upgrade project. Likely, the degree of change impacting the project is low. Which of the following is the best lifecycle choice for this scenario?
- Iterative
- Agile
- Predictive
- Incremental
Explanation: A predictive lifecycle is suitable when the degree of change is low, as it follows a clear, sequential plan with well-defined requirements.
Question 5)
Another project’s customer requests a high degree of deliveries. However, the team anticipates the degree of change to be high as well. Which of the following is the best lifecycle choice for this scenario?
- Incremental
- Predictive
- Agile
- Iterative
Explanation: Agile is ideal for projects with frequent deliveries and a high degree of change, as it promotes flexibility and iterative progress.
Question 6)
A project manager is overseeing a project and decides to use a Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control Model. Which of the following types of project is the manager overseeing?
- Lean
- Six Sigma
- Waterfall
- Agile
Explanation: The DMAIC model is a core component of Six Sigma, focusing on process improvement and reducing defects.
Question 7)
The project management team is reviewing a variety of organizational types. Which two of the following ways will the project manager be impacted depending on the organization type the team selects?
- Project manager’s authority
- Resource availability
- Contingency reserves
- Risk appetite
Explanation: The organizational type determines the project manager’s authority and the availability of resources, influencing how projects are managed.
Question 8)
A project manager works in an organization sometimes known as a “silo.” In this model, support is minimal, and the manager may not be assigned as a project manager. Success in this model is difficult to achieve. Which model fits this scenario?
- Organic or functional
- Weak matrix
- Strong matrix
- Project oriented
Explanation: Organic or functional organizations have a hierarchical structure, with minimal cross-departmental collaboration and limited support for project management roles.
Question 9)
A project management office (PMO) has a low level of control but does provide best practices, common oversights, and templates. Which type of PMO is this?
- Controlling
- Directive
- Supportive
- Informational
Explanation: A supportive PMO offers guidance, templates, and best practices but does not enforce strict control over projects.
Question 10)
A key infrastructure project has failed twice to achieve the desired objectives. For the third attempt, the team modifies their approach to meet the needs of the project. What method did the team use in this scenario?
- Updating
- Modifying
- Revising
- Tailoring
Explanation: Tailoring involves customizing project processes and methodologies to better fit the project’s unique requirements and circumstances.
Module 3 Graded Quiz: Modern Project Management Quiz Answers
Question 1)
A key principle in project management states that the ability to absorb impacts and recover quickly is essential. What does the Project Management Institute (PMI) call this ability?
- Resiliency
- Flexibility
- Strength
- Adaptability
Explanation: PMI defines resiliency as the ability to adapt, recover, and maintain progress despite setbacks, making it essential for project success.
Question 2)
A team is trying to understand how all process groups work together. They also need to develop and implement an integrated change control process. Which knowledge area are they analyzing?
- Project integration management
- Project initiation management
- Project planning management
- Project scope management
Explanation: Project integration management focuses on ensuring all processes work together and includes the integrated change control process.
Question 3)
There are a number of meetings that are critical to success when managing an adaptive project. Which two meetings are appropriate for an adaptive project?
- Product backlog refinement
- Kick-off meetings to gain stakeholder acceptance
- Pre-baseline and baseline presentations
- Daily standup meeting
Explanation: Adaptive projects use agile practices like product backlog refinement and daily standups to prioritize tasks and ensure continuous progress.
Question 4)
One of the 12 Principles of Project Management describes each project as unique, recommends that the project manager avoid a “Cookie Cutter” approach, and directs managers to adapt their approach to meet the project’s needs. Which principle does this describe?
- Navigate complexity
- Recognize, evaluate, and respond to system interactions
- Optimize risk responses
- Tailor based on context
Explanation: The principle of tailoring advises adapting project management practices to the specific context of the project to maximize effectiveness.
Question 5)
The 7-Step Performance Model walks project managers through the process of how to build an effective and high-performing team. Steps 1-4 of this model share stages to create the team. Steps 5-7 share project team sustainability and performance actions. Who developed this 7-Step Performance Model?
- Douglas McGregor
- David McClelland
- Abraham Maslow
- Drexler and Sibbit
Explanation: Drexler and Sibbit created the 7-Step Performance Model to help teams achieve high performance through clear stages of development and sustainability.
Question 6)
Management assumes all employees work for the sole purpose of income. Managers should influence these team members using a hands-on and top-down management approach. Which of the following management type does this describe?
- Theory D
- Theory X
- Theory Z
- Theory Y
Explanation: Theory X assumes employees are motivated by financial rewards and require direct supervision, emphasizing a controlling management style.
Question 7)
Which of the following quality tools provides the horizontal value chain for a process from start to end and is commonly used by Six Sigma for process development and improvement?
- Mind mapping
- SIPOC
- Design for X
- Logical data model
Explanation: SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers) is a Six Sigma tool that outlines process steps from start to finish to improve quality.
Question 8)
The team uses a graphical representation of numerical data over a standard distribution. They determine the mean and analyze how data changes as you move away from the mean on the bell curve. Which tool and technique is the team using?
- Histogram
- Scatter diagram
- Affinity chart
- Design for X
Explanation: Design for X focuses on optimizing variables across a standard distribution, often utilizing a bell curve for analysis.
Question 9)
William Bridges developed a three-step transition model that defines stages of change. Which of the following is the final stage in this three-step transition model?
- The Neutral Zone
- The New Beginning
- Ending, Losing, and Letting Go
- Unfreezing
Explanation: The New Beginning represents the final stage in Bridges’ transition model, signifying acceptance of and engagement with the change.
Question 10)
Which two of the following choices explain the quality control function?
- Uses quality audits
- Corrective
- Prevention
- Uses inspections
Explanation: Quality control involves inspections to identify defects and corrective actions to address them, ensuring deliverables meet project standards.
Module 4 Graded Quiz: Setting up the project for success Quiz Answers
Question 1)
A critical stakeholder’s responsibilities to support a project include ensuring that the project team produces the deliverables and meets the timeline. Which of the following roles should the project manager annotate on the stakeholder register for the stakeholder in this scenario?
- R
- C
- I
- A
Explanation: “R” (Responsible) indicates the stakeholder who ensures deliverables are produced and timelines are met.
Question 2)
The project manager has completed the project charter, and the team has just finished a brainstorming session to identify key stakeholders critical to the project’s success. Where should the project manager document these stakeholders?
- Stakeholder dictionary
- Stakeholder matrix
- Stakeholder log
- Stakeholder register
Explanation: The stakeholder register is the document where key stakeholders and their roles are recorded and managed.
Question 3)
Which of the following is a weighted method of decision-making in which two or more options are compared and scored?
- Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis
- OARP
- Wideband Delphi
- Nominal Group Technique
Explanation: Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis evaluates options based on weighted criteria, helping to make decisions systematically.
Question 4)
A project team employs a voting method where more than 50% of the voting members determine the decision path. Which of the following criterion describes this scenario?
- Unanimity
- Unilateral
- Plurality
- Majority
Explanation: A majority vote requires more than 50% agreement to make a decision.
Question 5)
Review the illustration. Which of the following is the name of this tool?
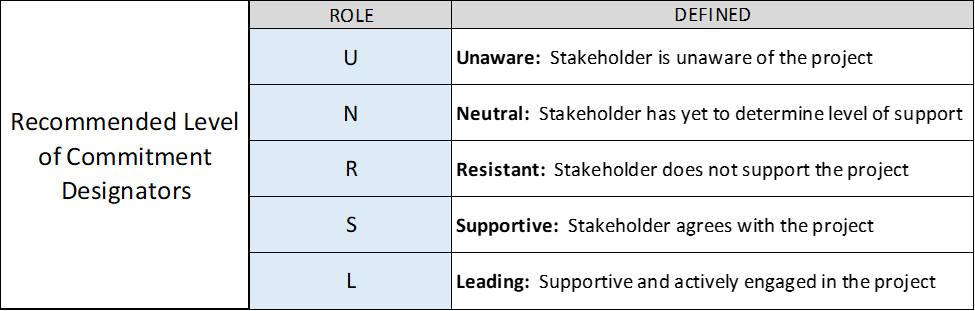
- Strategy development table
- Commitment level matrix
- UNRSL analysis tool
- Stakeholder engagement assessment matrix
Explanation: The stakeholder engagement assessment matrix tracks stakeholders’ levels of engagement throughout the project lifecycle.
Question 6)
There are two projects. Project A has a value of $60,000. Project B has a value of $40,000. You can select only one project, and you decide on Project B. By selecting Project B, you “give up” the chance to gain the value of Project A. Which of the following concepts addresses project trade-offs like the one in this scenario?
- Time value of money
- Opportunity cost
- Depreciation
- Straight line
Explanation: Opportunity cost refers to the value of the next best alternative foregone when making a decision.
Question 7)
A project manager discovers that cash flow may be increased by applying tax benefits gained from asset depreciation. The project manager purchased a capital asset valued at $20,000 with a depreciable lifecycle of 4 years. How much can the manager claim each year using the straight-line depreciation method?
- $10,000
- $20,000
- $5,000
- $7,500
Explanation: Using the straight-line depreciation method, the yearly depreciation is calculated as $20,000 ÷ 4 = $5,000.
Question 8)
A project has benefits of $100,000. The costs are $50,000. Which is the benefit-cost ratio (BCR) for this scenario?
- $50,000
- 100%
- 0.5
- 2.0
Explanation: The BCR is calculated as Benefits ÷ Costs, which is $100,000 ÷ $50,000 = 2.0.
Question 9)
Which of the following estimation techniques uses regression analysis and learning curve techniques to multiply the quantity of work performed times the productivity rate?
- Bottom-up
- Top-down
- Parametric
- Expert
Explanation: Parametric estimation uses mathematical models like regression analysis to calculate project costs or durations based on known quantities and rates.
Question 10)
The project manager normally provides the rough order of magnitude (ROM) estimate in the project charter. What is the range for a ROM estimate?
- -5%/+10%
- -10%/+10%
- -25%/+25%
- -25%/+75%
Explanation: ROM estimates typically range from -25% to +25%, providing an early approximation of project costs.
Module 5 Graded Quiz: Project Planning Quiz Answers
Question 1)
The sponsor approves the project charter, and the project manager publishes the stakeholder register. Which planning process should the team address first?
- Cost
- Scope
- Quality
- Schedule
Explanation: Scope planning is foundational as it defines the project’s deliverables and work boundaries before addressing costs, quality, or schedule.
Question 2)
The project team is planning the scope and are working on a document that shows the detail and attributes of each work package supporting the project. These attributes are broken into specific tasks. Which document is under development in this scenario?
- Project charter
- Work breakdown structure (WBS) dictionary
- Scope statement
- Work breakdown structure (WBS)
Explanation: The WBS dictionary provides detailed descriptions and attributes of each work package and its associated tasks.
Question 3)
Which two of the following components are part of the overall scope baseline?
- Requirements management plan
- Work breakdown structure (WBS) dictionary
- Scope management plan
- Scope statement
Explanation: The scope baseline includes the scope statement, WBS, and WBS dictionary, serving as the reference for all scope-related work.
Question 4)
The project management team develops a comprehensive network diagram to support the project. Which two of the following choices would be featured on a network diagram in this scenario?
- Task descriptions
- Critical path
- Resource costs
- Work package durations
Explanation: Network diagrams feature the sequence of activities, durations, and dependencies, including the critical path.
Question 5)
A project team analyzes all costs and determines a few indirect costs. Which item would fall under this category?
- Equipment acquisitions
- Company-funded training
- Material purchases
- Contingency reserves
Explanation: Indirect costs, such as training or utilities, are not directly tied to a specific project deliverable but benefit the overall project or organization.
Question 6)
A project manager estimates project cost with an optimistic cost of $22,000, a most-likely cost of $28,000, and a pessimistic cost of $40,000. Applying the PERT method of three-point estimation, which cost estimate should the project manager use?
- $28,000
- $29,000
- $40,000
- $30,000
Explanation: PERT estimation formula:
(Optimistic+4×Most Likely+Pessimistic)/6=(22,000+4×28,000+40,000)/6=29,000(Optimistic + 4 \times Most\ Likely + Pessimistic) / 6 = (22,000 + 4 \times 28,000 + 40,000) / 6 = 29,000.
Question 7)
Plans and timing to support deliverable inspections and verify newly produced deliverables are included in which plan?
- Quality assurance plan
- Quality management plan
- Project measurement plan
- Quality control plan
Explanation: The quality management plan outlines processes for ensuring deliverables meet quality standards, including inspections and verification.
Question 8)
What is the CV for the following scenario?
EV=3,000EV = 3,000, PV=2,800PV = 2,800, AC=2,700AC = 2,700
- +$300
- +$200
- -$300
- -$200
Explanation: Cost Variance (CV) = EV−AC=3,000−2,700=+300EV – AC = 3,000 – 2,700 = +300.
Question 9)
What is the SPI for the following scenario?
EV=3,000EV = 3,000, PV=2,800PV = 2,800, AC=2,700AC = 2,700
- 1.11
- 1.07
- 0.96
- 1.04
Explanation: Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = EV/PV=3,000/2,800=1.07EV / PV = 3,000 / 2,800 = 1.07.
Question 10)
Using the following choices, fill in the two blanks in the statement. A manager schedules the project kick-off meeting after _______ approval of the project management plan. The meeting strives to gain ________ acceptance.
- sponsor, stakeholder
- project team, sponsor
- sponsor, project team
- stakeholder, sponsor
Explanation: The sponsor approves the project management plan, and the kick-off meeting is held to gain stakeholder buy-in and acceptance.
Peer-graded Assignment: Project Initiation and Set-Up Assignment Answers | Link updated Soon
Read also: Introduction to Project Management Quiz Answers
Final Exam: Project Management Foundations Initiation and Planning Quiz Answers
Question 1)
Many project managers worry about managing the triple constraints. The Project Management Institute (PMI) refers to this as the project manager’s triangle. Which of the following two constraints apply to this description?
- Cost
- Scope
- Risk
- Communications
Explanation: The triple constraints include scope, cost, and schedule, which form the project management triangle.
Question 2)
The project management framework is divided into five distinct phases: initiate, plan, execute, monitor, control, and close. How does the PMI refer to these phases?
- Project process groups
- Project lifecycles
- Project steps
- Project phase gates
Explanation: PMI defines these five phases as “process groups” to describe the flow of activities in project management.
Question 3)
The project management framework developed by the PMI lists forty-nine specific processes. Where do the majority of these processes fall within the framework?
- Plan
- Initiate
- Monitor and Control
- Execute
Explanation: Most project management processes fall under the “Plan” process group, emphasizing detailed planning before execution.
Question 4)
The ABC Company recently implemented a Project Management Office (PMO). The initial plan is for this PMO to provide information, standard templates, and guidance to the firm’s project managers. What type of PMO does this scenario describe?
- Supportive
- Informational
- Directive
- Controlling
Explanation: A supportive PMO provides guidance, templates, and expertise to project managers without enforcing strict oversight.
Question 5)
The PMI breaks project management lifecycles into adaptive and predictive categories. Which two project management models fall under the predictive category?
- Scrum
- Waterfall
- Agile
- Six Sigma
Explanation: Predictive models like Waterfall and Six Sigma rely on detailed upfront planning and predefined processes.
Question 6)
A team plans to implement an agile model to support certain projects in an organization. Where will the team maintain and document all requirements?
- In the scope backlog
- In the scope statement
- In the scope management plan
- In the product backlog
Explanation: Agile projects maintain requirements in a dynamic product backlog, which is updated iteratively.
Question 7)
Ralph Stacey developed an analysis matrix to determine the optimal lifecycle to choose to implement a project. What are the two criteria Stacey recommends to make this decision?
- Technical degree of uncertainty
- Requirements uncertainty
- Overall risk exposure and score
- Scheduling volatility
Explanation: Stacey’s matrix evaluates technical complexity and uncertainty in requirements to determine project approach.
Question 8)
A project sponsor reviewed a list of key roles supporting an agile project. He notices that the list includes more than one role. What role is not included on the agile supporting role list?
- Product owner
- Development team
- Project manager
- Scrum master
Explanation: Agile frameworks, such as Scrum, typically do not include the project manager role as it focuses on team empowerment.
Question 9)
Which two of the following options are formal phases in the PMI project management lifecycle?
- Implement
- Manage
- Initiate
- Execute
Explanation: PMI lifecycle phases include Initiate, Plan, Execute, Monitor and Control, and Close.
Question 10)
The PMI stresses the impact that organization models can have on a project and the team. They define three distinct matrix models. In one of the models, the project manager enjoys power more than the functional manager, can make decisions on the allocation of resources, has a great deal of control, and can utilize their project management skills on the projects. Which matrix model does this describe?
- Weak Matrix Model
- Balanced Matrix Model
- Standard Matrix Model
- Strong Matrix Model
Explanation: The strong matrix model grants more authority to project managers over resources and decisions.
Question 11)
A team is performing a cost of quality study and analyzing costs of non-compliance against costs of compliance. Which two costs are non-compliance?
- Warranty claims costs
- Training costs
- Verification costs
- Reworks costs
Explanation: Costs of non-compliance include failure costs such as warranty claims and rework.
Question 12)
A product owner is analyzing the transition model for change due to changes happening on the project. Some people’s productivity is dropping due to frustration or confusion. Others seem to be motivated, creative, and passionate. What stage of the transition model is the team in?
- The New Beginning
- The Neutral Zone
- Transition
- Ending, Losing, and Letting Go
Explanation: The Neutral Zone represents a phase of uncertainty and creativity during a transition.
Question 13)
Current ABC Company management assumes employees are motivated from within. They use a more personal coaching style to influence the team. What is this management style?
- Theory Z
- Theory W
- Theory X
- Theory Y
Explanation: Theory Y assumes employees are self-motivated and require encouragement rather than control.
Question 14)
When managing the virtual team, which skill is most critical to success?
- Motivation
- Communications
- Coaching
- Influencing
Explanation: Effective communication is the most critical skill for managing distributed virtual teams.
Question 15)
A project manager wants to create a learning environment where the team can attain new skills and grow, provide continual performance feedback, and communicate effectively to manage issues as they occur. Which knowledge area should the project manager consult for guidance?
- Quality management
- Resource management
- Communications management
- Integration management
Explanation: Resource management focuses on team development, feedback, and conflict resolution.
Question 16)
A project manager reviews critical financial metrics. Which two of the following metrics are not impacted by the time value of money?
- ROI
- IRR
- NPV
- Payback
Explanation: ROI and payback do not consider the time value of money, unlike IRR and NPV.
Question 17)
A project manager will need to acquire some key materials which the project will fund. How should the project manager categorize these costs?
- Direct costs
- Contingency costs
- Indirect costs
- Reimbursable costs
Explanation: Direct costs are directly attributable to the project, such as material acquisitions.
Question 18)
A project manager analyzes key project stakeholders and develops strategies to ensure desired commitment levels are met. What plan did the project manager develop?
- RACI chart
- Resource register
- Stakeholder register
- Stakeholder engagement plan
Explanation: The stakeholder engagement plan outlines strategies to manage stakeholder expectations and commitments.
Question 19)
Which of the following is true regarding the stakeholder register?
- The project manager updates the stakeholder register throughout the project.
- The project manager uses the stakeholder engagement plan to fill out the stakeholder register.
- The project manager accomplishes the stakeholder register in the planning process group.
- The project manager completes the stakeholder register before publishing a project charter.
Explanation: The stakeholder register is a dynamic document updated throughout the project.
Question 20)
A project sponsor uses a fast-decision-making method where an individual makes all the decisions. However, there are risks associated with this method. Which decision-making method is the sponsor using?
- Plurality
- Autocratic
- Unanimity
- OARP
Explanation: Autocratic decision-making places authority with one individual, enabling quick decisions but introducing risks.
Question 21)
Bethany schedules a project kick-off meeting. What are the two primary purposes of this meeting?
- To introduce the project charter
- To gain stakeholder acceptance
- To gain sponsor approval
- To formally enter the executing phase
Explanation: Kick-off meetings aim to gain stakeholder acceptance and mark the project’s transition into execution.
Question 22)
A team recently completed Earned Value analysis of a project. The CPI was .91. The SPI was 1.06. What is the status of this project?
- Behind on schedule and behind on budget
- Ahead of schedule and ahead of budget
- Behind on schedule but ahead of budget
- Ahead of schedule but behind budget
Explanation: A CPI of 0.91 indicates over-budget performance, while an SPI of 1.06 indicates ahead-of-schedule performance.
Question 23)
A project manager develops a simple “how-to” plan that provides process and direction to the team on how to define, develop, monitor, control, and validate the project schedule. Which of the following plans is being described?
- Schedule process plan
- Schedule model
- Schedule critical path analysis
- Schedule management plan
Explanation: The schedule management plan outlines how to develop, manage, and monitor the project schedule.
Question 24)
A project manager and team are currently developing support plans for the overall project management plan. Which two of the following plans should the manager place in the support planning folder?
- Cost management plan
- Quality management plan
- Scope management plan
- Communications management plan
Explanation: Support plans include cost and quality management plans, which provide frameworks for tracking resources and quality.
Question 25)
The project team completes scope planning and develops a document that is said to be the most detailed version of the scope. Which document did the team produce?
- Project scope statement
- Work breakdown structure (WBS)
- Scope management plan
- Project network diagram
Explanation: The WBS is the most detailed depiction of the project’s scope, breaking it into manageable components



